ILDs, WHICH INCLUDE IPF AND PPF, ARE COMPLEX, LIFE- THREATENING CONDITIONS1
CURRENT CHALLENGES
There are unmet needs for patients with IPF and PPF.2-4 Patients experience irreversible lung damage, resulting in a significant disease burden.3,5,6 They may face reduced ability to work or to complete tasks of daily living, an increased risk of hospitalization, and an increased risk of death.7-10
PROGRESSIVE PULMONARY FIBROSIS IS A THREAT ACROSS A RANGE OF ILDs11,12
IPF is the prototypical progressive fibrosing ILD, and PPF refers to any non-IPF progressive fibrotic ILD, including the range of autoimmune ILDs.11,12 PPF is not confined to patients with a UIP pattern, but also occurs in those with an NSIP pattern on HRCT.13
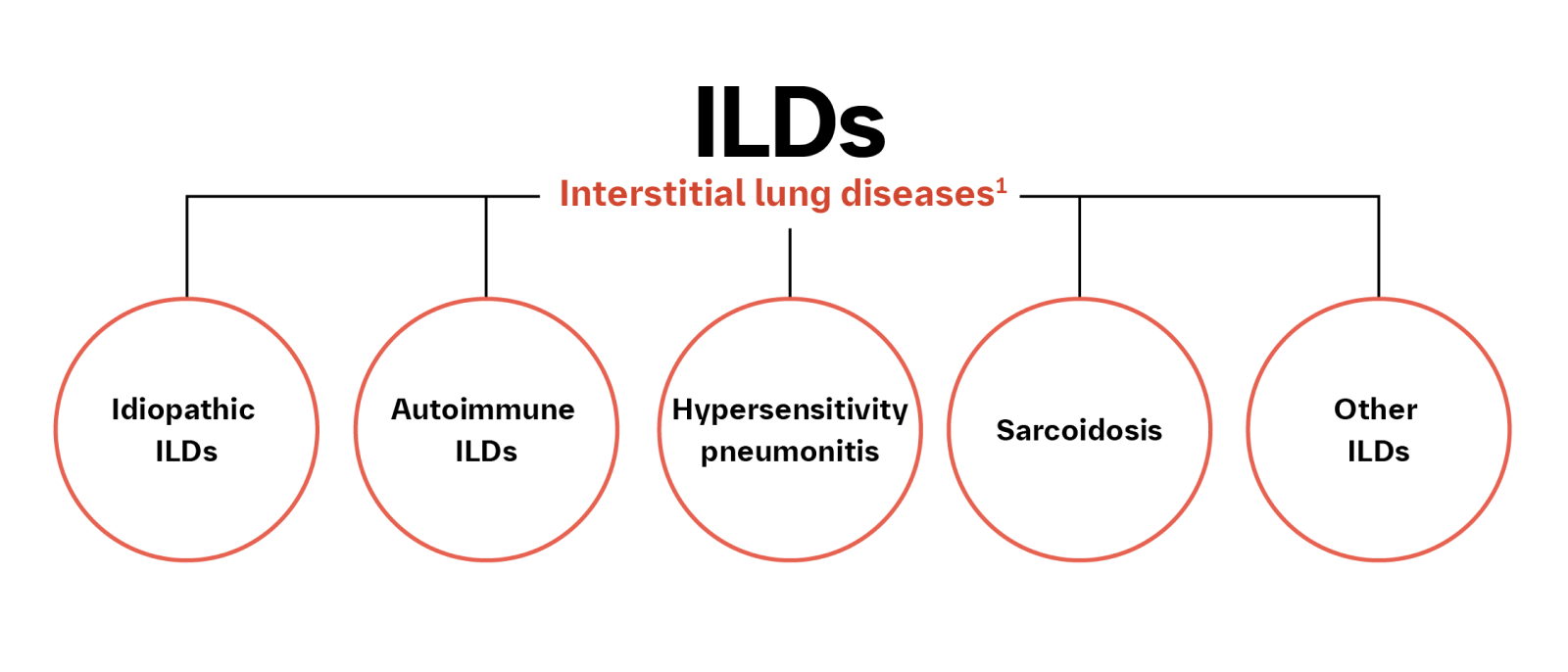
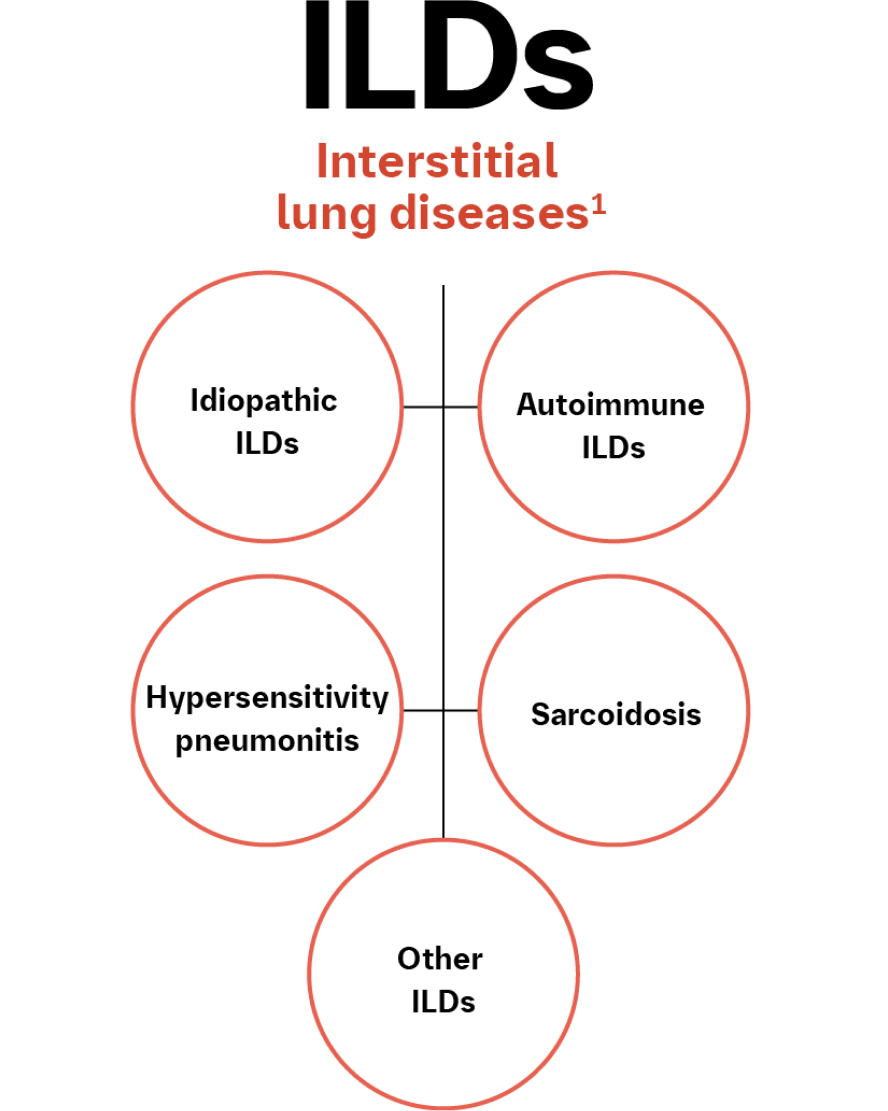
Disease progression is comparable between IPF and PPF and is characterized by worsening respiratory symptoms, decreased lung function, and radiological evidence of increased extent of fibrosis.12
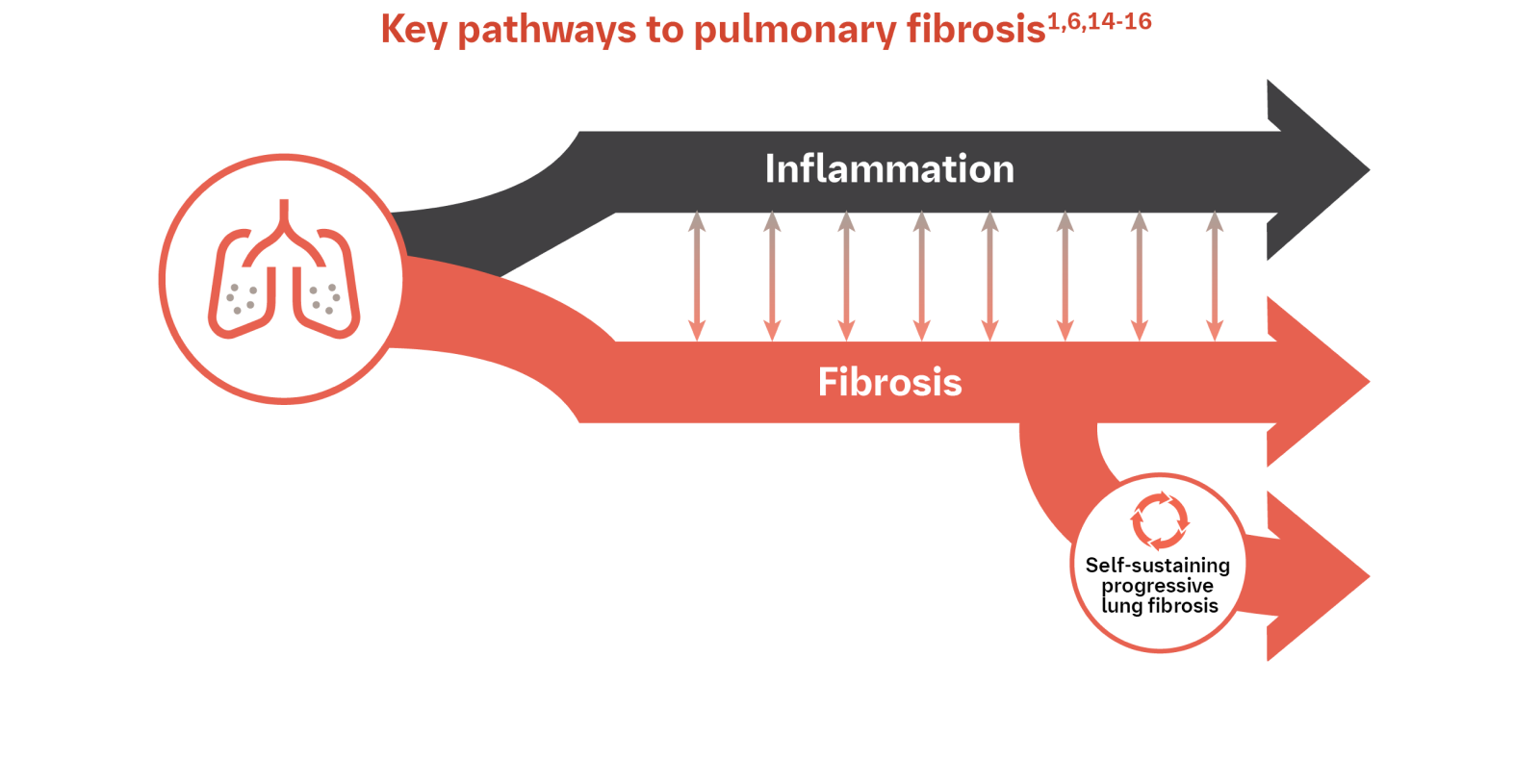
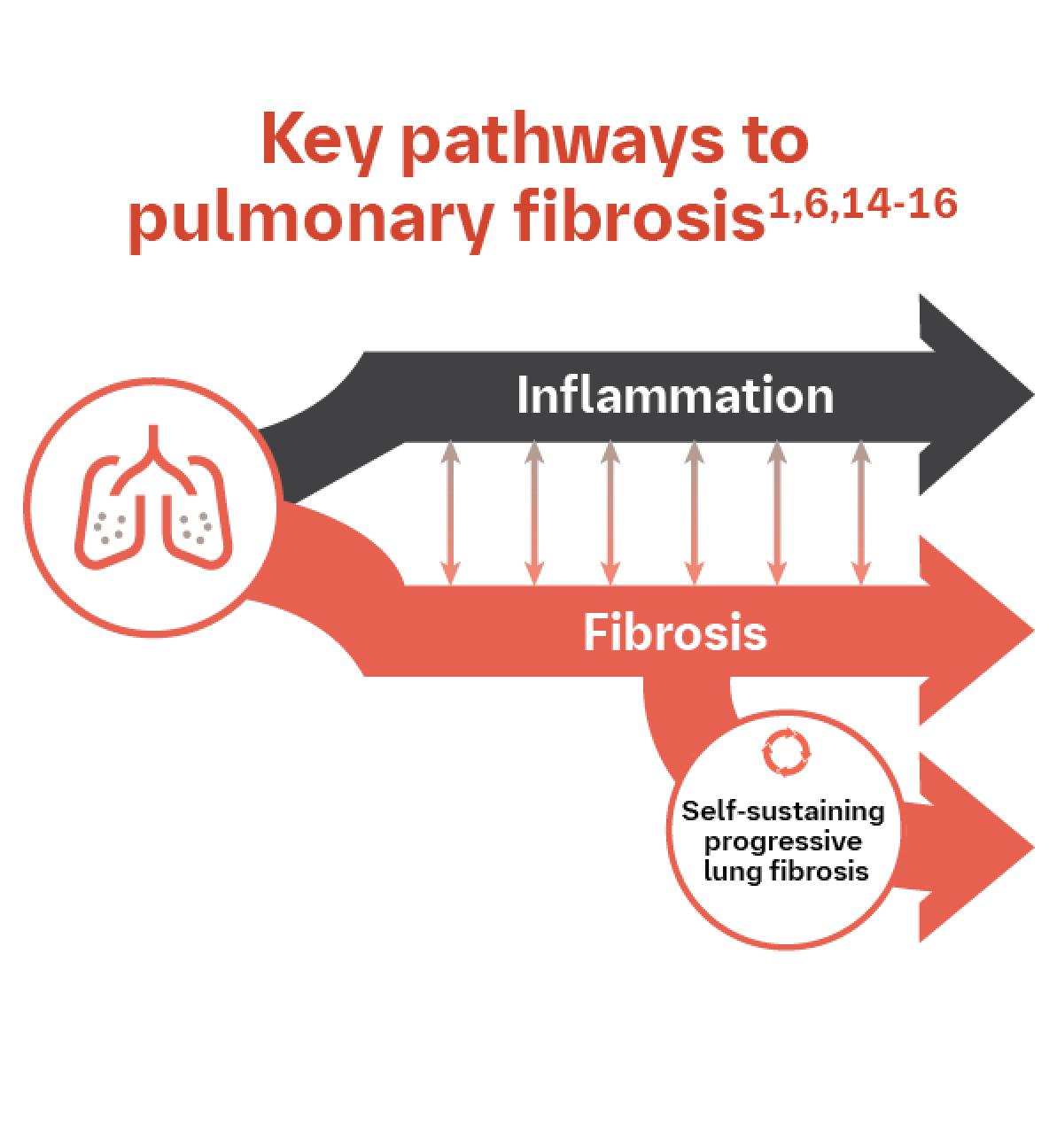
EVOLVING UNDERSTANDING OF THE MECHANISMS OF PULMONARY FIBROSIS2,3
The underlying mechanisms of pulmonary fibrosis are complex and not fully understood.2,3 ILDs encompass a spectrum of disorders that are driven by the interplay of inflammation and fibrosis.1,6,14,15 Regardless of initial cause, fibrotic pathways can progress independently of inflammation and become self-sustaining.6,15,16
FIBROSIS IS OCCURRING EARLY, EVEN IN AUTOIMMUNE ILDs17,18
In autoimmune diseases, the underlying pathogenesis involves the interplay of inflammation and fibrosis early in the course of the disease, making proactive screening for ILD essential.17-19*
*Risk factors for the development of ILD include demographics, disease manifestations, and antibody profile.19
HRCT, high-resolution computed tomography; IPF, idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis; NSIP, nonspecific interstitial pneumonia; PPF, progressive pulmonary fibrosis; UIP, usual interstitial pneumonia.
Continuing to understand the complex interplay between inflammation and fibrosis in the progression of pulmonary fibrosis is important.